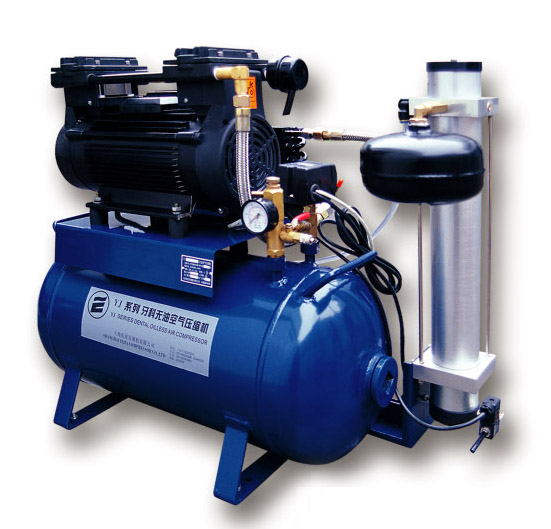
Beijing air pump sales (air compressor) Sales: 13701207296
**Beijing Air Pump (Air Compressor) Sales: 13701207296**
### Selection of Air Pump / Air Compressor
The selection of an air compressor mainly depends on the working pressure and flow rate of the pneumatic system.
The working pressure of the air source should be about 20% higher than the highest working pressure in the pneumatic system, as it needs to account for the pressure drop along the supply pipe and local losses. If some parts of the system require lower working pressure, a pressure-reducing valve can be used to supply air. The rated exhaust pressure of air compressors is divided into low-pressure (0.7~1.0 MPa), medium-pressure (1.0~10 MPa), high-pressure (10~100 MPa), and ultra-high-pressure (above 100 MPa). The appropriate type can be selected based on actual needs. Commonly used pressures are generally between 0.7-1.25 MPa.
First, select the type of air compressor according to its characteristic requirements. Then, determine the output pressure (pc) and suction flow rate (qc) of the air compressor based on the working pressure and flow rate required by the pneumatic system, and finally choose the model of the air compressor.
1. **Output Pressure of the Air Compressor (pc):**
pc = p + ∑△p
- pc: Output pressure of the air compressor
- p: Maximum operating pressure of the pneumatic actuator
- ∑△p: Total pressure loss in the pneumatic system
In general, ∑△p = 0.15~0.2 MPa.
2. **Suction Flow Rate of the Air Compressor (qc):**
Without a storage tank: qb = qmax
With a storage tank: qb = qsa
- qb: Flow rate provided by the pneumatic system
- qmax: Maximum air consumption of the pneumatic system
- qsa: Average air consumption of the pneumatic system
Suction flow rate of the air compressor: qc = kqb
- qc: Suction flow rate of the air compressor
- k: Correction factor. This mainly considers factors such as leakage at pneumatic components and pipe joints, estimation errors in the air consumption of the pneumatic system, utilization rate when multiple pneumatic devices are not used simultaneously, and the possibility of adding new pneumatic equipment. Generally, k = 1.5~2.0.
3. **Power of the Air Compressor (P):**
P = (n+1) * k * p1 * qc * (pc/p1)^{[(k-1)/[(n+1)*k]-1} / (k-1) * 0.06
---
### Uses of Air Pump / Air Compressor
a. Traditional pneumatic power: Pneumatic tools, rock drills, jackhammers, pneumatic wrenches, pneumatic sandblasting
b. Instrument control and automation devices, such as tool changing in machining centers
c. Vehicle braking, opening and closing of windows and doors
d. Jet looms use compressed air to blow weft yarn instead of shuttles
e. Food and pharmaceutical industries, using compressed air to stir slurry
f. Starting large marine diesel engines
g. Wind tunnel experiments, underground passage ventilation, metal smelting
h. Oil well fracturing
i. High-pressure air blasting for coal mining
j. Weapon systems, missile launching, torpedo launching
k. Submarine buoyancy control, salvage of sunken ships, underwater oil exploration, air cushion boats
l. Tire inflation
m. Painting with spray guns
n. Bottle blowing machines
---
This concludes the translation. Let me know if you need further clarification!